What Are Altchains?
Altchains is an abbreviation for “alternative blockchains,” which refers to any blockchain other than Bitcoin or Ethereum. Altchains emerged in 2021 due to the scaling and transaction fee challenges facing Ethereum, and altchain dev teams have grasped this opportunity to build out more scalable and cheap blockchains to compete with Ethereum. You may have heard of Terra or Avalanche or Solana, which are just two of the many altchains that exist today. To fully understand altchains, you should first grasp the following concepts.
Layer 0
Layer 0 refers to a protocol that enables layer 1 (L1) solutions to interact on the same network. Layer 0 is the foundation of L1 blockchains, allowing the entire blockchain to be built on top of it. The Polkadot network is an example of a layer 0 protocol.
Layer 1
The term “layer-1” (or L1) refers to the underlying main blockchain network in a decentralized blockchain ecosystem. Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Solana are examples of layer-1 blockchains.
Layer 2/Sidechains
On the other hand, “layer-2” (L2) refers to a third-party integration that works on top of a layer-1 blockchain to help scale an application by processing transactions off of the main blockchain (L1) while maintaining the same security and decentralization. Arbitrum is an example of an Ethereum L2 scaling solution.
A sidechain is a separate blockchain that works independently parallel to the main L1 chain, e.g. Ethereum. The primary distinction between sidechains and most layer 2 solutions is that sidechains are different blockchains linked to the mainchain, and have their own consensus algorithm features. In contrast, layer 2 solutions are constructed as mainchains extensions and rely on their security structure. Examples of sidechains are Polygon for Ethereum, and DeFi Chain for Bitcoin.
Altcoins
Altcoins, short for “alternative coins,” are all cryptocurrencies other than Bitcoin. Altcoins are classified into several types: utility tokens, DeFi tokens, NFT tokens, stablecoins, meme tokens, etc. Most altcoins do not have their own blockchain and are usually minted on altchains.
EVM
Ethereum developed the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), a virtual environment that allows developers to develop smart contracts on Ethereum. EVM enables smart contracts to have more functionality without being unnecessarily complex. You may find a list of EVM-powered blockchains on Chainlist.
The purpose of writing this guide is to provide a pathway for beginners who might want to start exploring altchains. In some cases, a beginner may be starting from scratch and interacting with blockchains for the first time or might have already held some BTC or ETH and may want to explore other chains now. The table below is not meant to be exhaustive but merely to highlight the most popular ways people are interacting with altchains today.
How To Use Altchains?
1. Setup a wallet and obtain funds
i) Acquire initial crypto funds using a CEX
Given current high transaction fee challenges, absolute beginner crypto users (particularly those with small capital) should start their journey to begin using crypto on an Ethereum L2 / sidechain (e.g., Polygon, Arbitrum) or an L1 blockchain that charges low fees.
Solana will be used as an example in this article. First, purchase some SOL tokens through the CEX of your choice. In our table, we have shown some options for “fiat onramp,” meaning you can buy SOL directly using fiat currency. Alternatively, you might need some stablecoins to purchase SOL. Set the tokens aside after you’ve finished. Now, we will proceed to create your own Solana wallet and transfer your newly-bought SOL to it.
ii) Setup a private crypto wallet
To explore the blockchain you selected, you have to create a wallet that supports the blockchain. It is suggested for new users to start with a browser wallet. Certain wallets only work for certain chains, so we have provided a list above. For additional security, you should set up your browser wallet on a separate browser profile. To illustrate the key steps, w will use the Solana Phantom wallet and Chrome Browser in this section.
First, visit the Phantom wallet official website and click on the download button (or “add to Chrome”). You will be redirected to the Chrome Web Store. Follow the prompts to download the app and create a wallet. It is important to read all of the instructions to prevent any mistakes. Don’t forget to write down your mnemonic phrase (or private key) and store it somewhere secure.
Now, copy your wallet’s public address and use it to transfer funds from the centralized exchange to your wallet. It is critical that you double-check to ensure that the wallet address and the blockchain you choose in the CEX matches the address and blockchain of your wallet. If you unintentionally sent funds to the wrong address or the wrong blockchain, it’ll be impossible to claim it back.
2. Swap for altcoins
Transacting on a blockchain would typically incur transaction fees, which you often pay with the chain’s native tokens. For example, you need SOL tokens to pay for transaction fees when using the Solana blockchain (instead of, say ETH). Now that you have some SOL in your Phantom wallet, you can also use them to interact with dApps on Solana or swap SOL for any other altcoins on the Solana blockchain. For example, say you wanted to interact with Solend, a lending protocol on Solana. You can either use SOL to place collateral or swap to stablecoins such as USDT or USDC for placement.
To swap native tokens to altcoins, you need to use a Decentralized Exchange (DEX). In this example, we’ll look at Raydium (a DEX of Solana blockchain). Simply go to Raydium’s official website, connect your wallet, follow the prompts to set up the exchange, and swap for the cryptocurrencies you wish. The other DEXes technically work roughly the same.
Normally, if the pool is not pre-configured in the DEX, you can input a custom Token Contract Address to search for the token. However, if you receive the contract address from a third-party source, be wary of possible counterfeit token pool or honeypot scams.
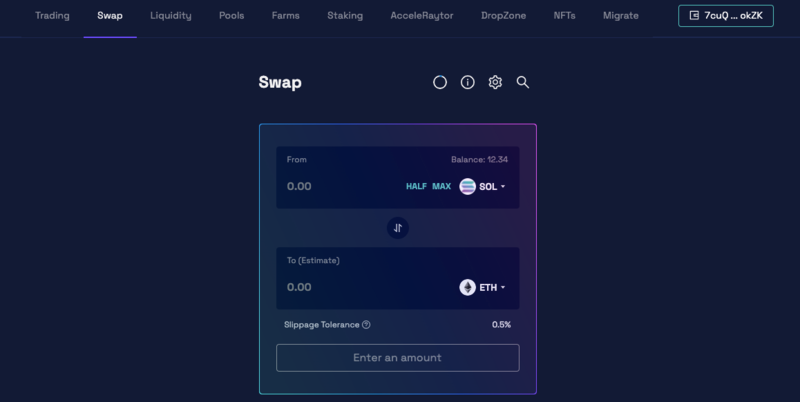
3. Bridge Tokens Across Different Chains
Usually, crypto users would have limited funds to explore different chains. If you wish to transfer your funds from one blockchain to another, there are two ways:
i) Through centralized exchanges
First, convert your funds into the native token or a stablecoin of your original blockchain (let’s say Blockchain A), then transfer the tokens to your CEX wallet. After that, use CEX to swap the token to the desired blockchain’s (let’s say Blockchain B) native tokens or stablecoins, then transfer them to your new blockchain wallet.
For instance, assume that you want to transfer funds from Solana to Ethereum mainnet using a CEX now:
Step 1 – Use a Solana DEX to convert your funds into SOL tokens.
Step 2 – Transfer the SOL into your CEX wallet (under Solana Mainnet) and swap the ETH into SOL.
Step 3 – Withdraw the ETH tokens into your MetaMask wallet (under Ethereum Mainnet).
ii) Through Bridges
To begin, visit a reliable cross-chain bridge web application, connect your wallet, input the type and amount of assets, destination blockchain, and destination wallet address. Finally, follow the prompts to validate the transaction and claim your funds. It will take some time for the funds to migrate to your wallet in the second blockchain.
Assume we want to bridge SOL tokens from Solana to Ethereum mainnet right now, we will utilize Wormhole Bridge to accomplish this:
Step 1 – Navigate to the web application’s web page of Wormhole Bridge.
Step 2 – Connect your Phantom wallet and specify the type of funds as SOL as well as the amount you want to transfer. After that, link your MetaMask wallet and follow the prompts to pay some transaction fees.
Step 3 – Confirm the transfer and wait for the funds to enter the bridge.
Step 4 – Once the funds have entered the bridge, click “Redeem” to claim the funds.
Although it is not difficult to grasp how to use a bridge in general, most bridges work in many different ways. Thus, it is critical to thoroughly study the guide for the individual bridge and any instructions before using it.
Another important thing to note is that to claim tokens on the other end of the bridge (destination blockchain), you may need to pay gas fees as well. This means you may need some of the native destination chain tokens before using a bridge, if not, your tokens may well be stuck in the bridge until you can borrow some native tokens to claim them!
4. Use Explorers To Check Your Transactions Progress
Use blockchain explorers to review transaction status and history if you are unsure whether you have sent funds to the wrong wallets, if your transactions are stuck, or any other concerns. Simply enter your wallet’s public address in the explorer to view your latest transaction history.
Security Tips
The cryptocurrency market could be very profitable, but hacks and scams have also plagued the sector over the years. So what can you do to avoid compromising the security of your crypto accounts?
i) Use a cold wallet to protect your encryption key (private address or mnemonic key). You may write down the key on paper and put it somewhere secure, or you can use a hardware wallet such as the Ledger Nano.
ii) Avoid engaging with malicious websites. Before connecting your wallet, double-check all URLs. It is also recommended to separate your crypto browser profile from the browser profile you use for the other activities (e.g., Facebook, Youtube, etc.).
iii) If you possess a significant amount of funds, keep it in separate wallets using different mnemonic keys.
iv) Never respond to a stranger’s DMs, especially in Discord, Telegram, Instagram, Twitter, and email.
v) Change your passwords regularly. Use Have I Been Pwned to check if your private information is leaked in a data breach. Avoid using the same email or password that has been compromised.
Additional Resources
- @ashboyash Blockchain Onboarding Cheat Sheet:
Twitter thread; Google Sheet
- @Darrenlautf Crypto Basic Skill Tree:
Twitter thread
- Rango Multi-chain DEX Aggregator:
https://app.rango.exchange/ - FundMovr Bridges:
https://app.fund.movr.network/ - Li.Finance Bridges:
https://li.finance/swap







